Peer Review Process
The journal peer review process start after the author(s) submit their manuscript. However, the author need to check the author guidelines and JAARU policy before submit their manuscript.
Peer review is an integral part of scientific publishing that approves and increase the validity and quality of the manuscript. In general, reviewers are looking for originality, scientific significance, conciseness, precision, and completeness. Peer reviewers are experts who volunteer their time to help improve the manuscripts they review. By the end of the peer review process, the manuscript becomes more robust, clear to the reader, and useful.
It should be noted that all the communication regarding the peer review process will be sent to the corresponding author.
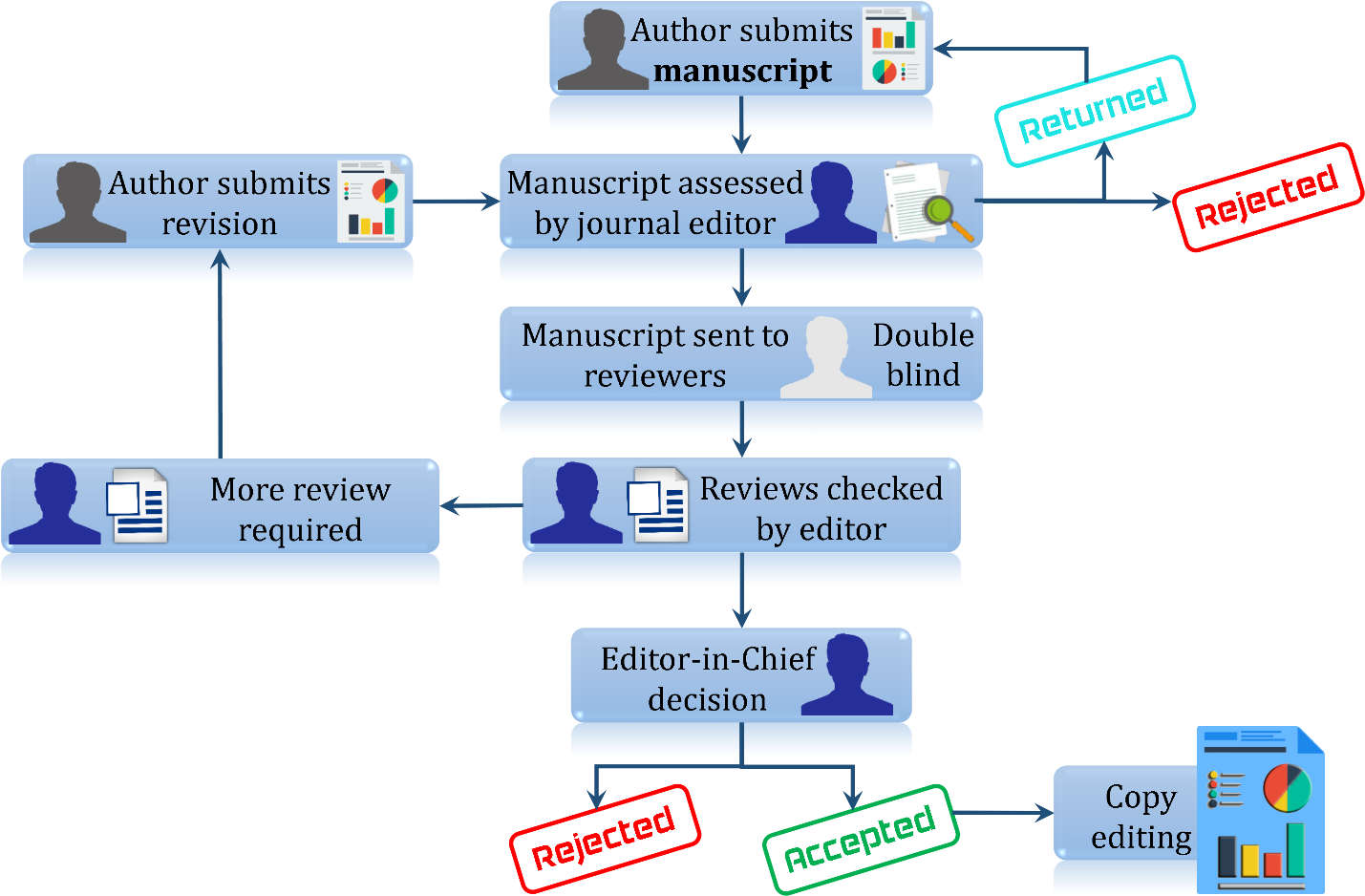
Concise flow diagram of the peer review process
The peer review process include:
- New submissions go through an in-house quality control check to ensure adherence to our policies and requirements, including:
- financial disclosures
- competing interests
- data deposition
Manuscripts will not be seen by an Academic Editor or peer reviewers until they pass this step.
JAARU aims to check manuscript as efficiently as possible. Though, timing may vary depending on whether manuscript need to be returned the submission to the author for follow-up queries or additional information.
The editor’s identity is anonymous to the author(s) throughout the peer review process.
- After a manuscript passes the quality control check (step 1), it is assigned to an Academic Editor according to relevant expertise. See the list of Editorial Board members. The Academic Editor is asked to evaluate the manuscript based on the JAARU criteria for publication. Editors can choose to perform the evaluation on the basis of their own expertise as well as assign external reviewers. After agreeing to review a manuscript, external reviewers are typically granted 4 weeks to complete the assignment. We will follow up with late reviewers and keep authors informed if there are any delays.
- When reviews received from experts, the Academic Editor assesses the reviews and decides whether reviews from additional experts are needed to evaluate the manuscript. Thereafter, a decision on a manuscript is made by the Academic Editor. After evaluation, the Academic Editor chooses between the following decisions:
- Accept
- Minor Revision
- Major Revision
- Reject
- In both revisions (Minor or Major) cases, the Academic Editor will send to the author the decision directly. The authors who receive a decision of revision (Minor or Major) will be given a specific time frame to resubmit their revised manuscript. After receiving the revised manuscript, commonly, the revised manuscript will be re-assigned to the original Academic Editor. The Academic Editor will determine if additional input is needed from reviewers.
- In Reject case, authors may submit a formal appeal for rejected manuscript. Appeal requests must be made in writing to [email protected] with the word “appeal” in the subject line. Authors must provide detailed reasons for the appeal and point-by-point responses to the reviewers' and/or Academic Editor's comments.
- In Accept case, it should be noted that the manuscript is provisionally accepted pending final check for formatting and technical requirements. Manuscript elements checked at this stage include:
- Author names and affiliations.
- Manuscript formatting.
- Figures and Tables.
- Data availability statement.
- Competing interest statement.
- Funding statement (conflict of interest).
To ensure prompt publication, manuscript will not be subject to detailed copyediting and author will not receive a typeset proof for review. Author will be able to review the final version of their manuscript when it is returned.

